All You Need To Know About Speed Cameras
Sunday, 21. March 2021
Following on from the last post the latest cameras are not the only one’s you should be wary of as speed cameras become more important as fewer police are seen on our roads catching speedsters.
In this report, prepared last year, there is everything you need to know about UK speed cameras, the types, how they work and what to look out for.
Speed cameras are unavoidably part of the UK motoring map, whether you think they’re a good thing or not. Those that use them would prefer they were known as safety cameras, as they’re designed to make UK roads safer, but whatever you want to call them, recent fake news reports about cameras on motorways like the M1 and M25 being set so they snap more motorists breaking the speed limit, show that they can still be misunderstood.
This guide helps you to know what to look out for where UK speed cameras are concerned. With police forces battling reduced funding, especially for road policing, speed cameras play a vital role in keeping a watchful eye on UK roads. Combined with local safety camera partnerships, they are a good visual deterrent and a reminder to check your speed when driving.
Some motorists see them as a revenue earner, though, as they can only catch speeders and are unable to spot unlicensed drivers, uninsured cars, drink and drug-drivers or general bad driving like road traffic officers are able to.
History of the speed camera
The first speed camera appeared in the UK in 1991 on the M40 motorway in West London. The cameras used rolls of film, which had to be developed and processed, and this also meant that there was a limit on how many speeders they could catch – it’s thought that the first camera used up its 400-exposure roll in 40 minutes after it was first switched on.
Over the years, new tech has been introduced, including forward-facing cameras and digital technology – so there’s no more need to change rolls of film, and means live cameras can be operated 24/7, uploading images directly to a central control room. Average speed cameras have also been introduced to monitor vehicle speed over longer distances, rather than just in one location, while traffic light and wrong-turn cameras have also been introduced.
We’ve also seen the introduction of cameras that no longer need a flash to snap speeding vehicles at night, while the latest mobile cameras operate over far longer distances than before. In this instance, if you’re speeding, the mobile camera could well have spotted you long before you’ve spotted it.
UK speed camera types explained
Here’s our guide to the different types of camera used on UK roads, and later we tell you what to expect if you think you’ve been caught speeding. The most common cameras in the UK are Gatso and Truvelo speed cameras, but there are more than a dozen different types of speed camera in use on UK roads in total. So without further ado, here’s what you should be looking for.
Gatso speed cameras

The Gatso was the first type of speed camera seen in the UK, and it’s still the most common type you’ll find. First introduced in 1991, the Gatso – short for Gatsometer, the name of the Dutch company that makes them – is a rear-facing camera.
That means it faces up the road and takes a picture of the rear of a speeding vehicle, so it can catch motorcycles as well as cars, vans and trucks.
A Gatso camera is easy to spot, as speed cameras must be painted yellow by law (in Scotland they have yellow and red diagonal stripes), although they can be obscured by road signs, street furniture and poorly maintained hedgerows.
Gatsos are usually mounted at the side of the road on a pole, although they can also be used in mobile units or on overhead gantries, such as you’ll find on the motorway.
Gatsos use radar to measure a vehicle’s speed, but the law says that there needs to be secondary proof of speeding. This is why all Gatso locations have dashed lines painted on the road in front of them.
These dashes are spaced evenly and are used to measure distance over time, so when a Gatso is activated it takes two pictures a fraction of a second apart, which can then be checked to see if an offence has been committed. The camera features a flash, and this goes off with each photo that’s taken.
On single carriageway roads, two sets of dashed lines are usually painted at a Gatso location. That means vehicles using either side of the road can be measured for speeding, but only in the direction that the Gatso is pointing. That means a camera site can only catch vehicles travelling away from it – if you are speeding towards one and it flashes, a ticket can’t be issued. Gatsos are also reliant on the dashed lines in the road – if the lines aren’t present, then the photos alone cannot be used to prosecute speeders.
While the first Gatso cameras used photographic film to record speeders, a new generation of digital camera arrived on 2007. These use a hard drive to store images and can be run 24/7 with a direct link to a control centre where the images are stored.
Truvelo speed cameras

The other common type of speed camera in the UK is the Truvelo, which is named after the South African company that makes it. While Truvelo cameras look similar to a Gatso because they are painted yellow and mounted on a pole, the chief difference between a Truvelo and a Gatso is that most Truvelo sites are forward facing.
As with a Gatso, a Truvelo camera uses a flash to get a clear image of a speeding vehicle’s number plate, but it also has a special filter on the flash that stops it from dazzling drivers. While this means that motorcycles (which lack front number plates) are harder to identify when speeding, the Truvelo can be used to identify the driver of a speeding vehicle.
The Truvelo only takes one picture, because the speeding offence is registered by sensors in the road which activate the camera. However, as with a Gatso, the photographic evidence needs backup, so small white squares are painted on the road where the sensors are to act as secondary evidence that a vehicle is speeding.
In recent years, the Truvelo has evolved into the Truvelo D-Cam. This is a digital version of the Truvelo that can be mounted forward or rear facing, can also be used at traffic lights, and can even be set up to watch up to 3 lanes at a time.
The D-Cam comes in a distinctive housing, while some have a flash unit separate from the camera itself – which again makes no visible light.
HADCES speed cameras

HADECS 3 stands for Highways Agency Digital Enforcement Camera System 3, which is the name given to the speed camera system that is being used on smart motorways across the country.
Hadecs units come in two small housings that are mounted on the side of motorway gantries. Thanks to their limited use of yellow to give away their location, and the fact they are about half the size of a Gatso or Truvelo camera unit, some people have called them stealth speed cameras, as they can be difficult to spot when travelling at 70mph.
Like other speed cameras, there are lines painted on the road that are used as secondary proof of speeding. And like a Gatso, Hadecs is a rear-facing radar camera, and it flashes when it picks up a vehicle travelling at more than the speed limit.

The innovation that allows Hadecs to be used on a smart motorway is its ability to adjust its detection speed according to the variable speed limit that’s posted. It does this by receiving information from sensors further along the carriageway, so when you see a lower limit posted on a smart motorway, the Hades cameras ahead can catch you for breaking it.
As well as speeding, Hadecs cameras can be set up to monitor up to five lanes, and they can detect vehicles that are using closed motorway lanes. As they are radar-based, they are able to work in all weather conditions, too.
SPECS speed cameras
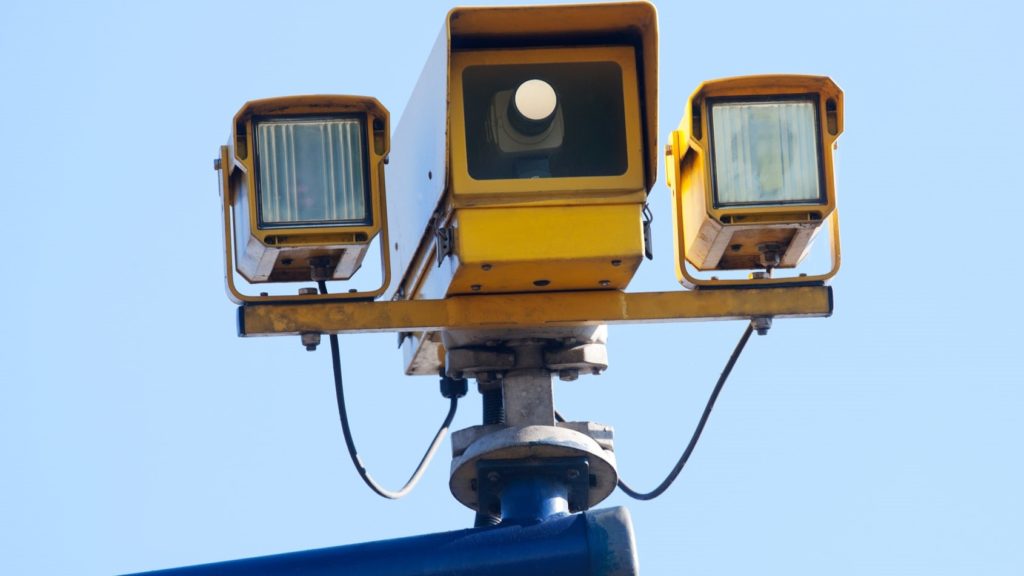

The SPECS camera system works differently because it measures vehicle speed over a far greater distance than a Gatso or Truvelo camera. You’ll see two or more sets of cameras to monitor vehicle speed for an extended distance, and this can be for as little as 200 yards or up to 99 miles – as the SPECS cameras on the A9 in Scotland do. SPECS cameras are often referred to as average speed cameras and are popular for use in roadworks where a lower speed limit than usual needs to be enforced.
SPECS uses Automatic Number Plate Reading (ANPR) tech to register vehicles as they pass. The first camera logs the vehicle with a time and date stamp. Once the vehicle has passed the second camera, the time stamps on the two images are compared, and if the time taken to cover the distance means the average speed is higher than the posted limit, then a ticket is issued.
You will usually find SPECS camera systems on motorways, especially in roadworks. And while some people think that weaving between lanes can help you pass them undetected, the truth is that the SPECS system can monitor multiple lanes. It’s also no use slowing for the cameras and then speeding between them, because the system measures your average speed between the two locations, not just how fast you’re going as you pass either camera.
Mobile speed camera vans

As well as these fixed speed cameras, many regions use mobile cameras to provide temporary coverage in areas where speeding is known to occur. Mobile units are usually located in vans that are marked as a safety camera vehicle with a bright livery, and they feature opening windows or panels to point the cameras through.
You will usually find them parked at the side of the road, in laybys (although not where parking restrictions apply) and also on bridges over roads.
The kind of cameras these mobile units use include mini Gatso cameras that use radar technology but there are also handheld radar or laser gun cameras. A laser gun uses a narrow laser beam that is reflected off a vehicle to measure its speed. These devices are quick and effective, being able to register a vehicle’s speed in as little as half a second and up to a distance of a mile away.
A radar gun works similarly to a laser gun. It has a wider beam and only works up to around 300 yards, while it will only come back with a reading after around 3 seconds, but it’s still an accurate way of registering a car’s speed.
Mobile camera vans can be set up in any direction to catch speeders, and can just as easily be set up to catch speeders approaching the camera site as going away from the site. As with fixed camera locations, a mobile camera site must have road signs indicating its presence, but apart from that, mobile cameras can be set up at any time.
In terms of location, mobile units are usually found in places notorious for accidents or speeding in the past, and are not normally pitched up in random places. Some local speed camera operators have been known to issue information on radio and social media to inform road users of where mobile camera units are operating on particular days.
Other speed cameras
Gatsos, Truvelos, SPECs and Hadecs 3 are the most common types of speed camera on UK roads, while other cameras that are available do a similar job. These are in addition to cameras which are used for traffic monitoring, catching vehicles that jump traffic lights (which incidentally aren’t required by law to be painted yellow) and cameras used by government agencies to check road tax and other ANPR-based activities.
Whichever way you look at it, the best way to ensure you’re not caught speeding is to remain aware of the speed limit and stick to it.
The big Speed camera questions answered
How do I know if a speed camera caught me?
If you have passed a speed camera that has flashed, the only way you will know for certain that you have been caught is when the registered keeper of the vehicle receives a Note of Intended Prosecution (NIP). This will arrive within 14 days of the offence taking place and will explain what happens next. This 14-day rule is in place so that companies, such as vehicle lease firms and car hire firms, can determine who was driving the vehicle at the time of the offence.
If you are the one that was caught speeding, then you will face a minimum fine of £100 and three points on your licence. If your driving licence is clean, then you may be offered the option of taking a speed awareness course instead of the penalty points.

As of 2017, the maximum fine for a speeding offence is up to £2,500 on the motorway. The amount you pay and the number of points you could face will depend on how much you were exceeding the speed limit by, as well as your level of income.
Do all speed cameras flash?
Most speed cameras flash when they capture an image, but you might not see the flash of a Truvelo forward-facing camera. That’s because forward-facing Truvelo cameras have a special filter over the flash to prevent dazzling oncoming drivers. If a camera is operating in good light conditions, the flash may not necessarily go off, either.
How do mobile speed cameras work?
Mobile speed camera units must be parked legally, either at the side of the road, in a layby or on a bridge, and operators must make motorists aware of their presence with the use of speed camera warning signs. That means they can operate in areas where the signs are already fixed, or they need to put up temporary signs nearby.
A speed camera van usually has openings at the rear or the side of the van for the cameras to have a clear line of sight of the road they are checking. Depending on the camera being used, the speed camera van can detect speeding vehicles up to two miles away on a clear day, especially with the latest camera technology being used.
The camera is operated either by a police officer or by a certified camera operator associated with a local speed camera partnership.
How can I avoid a speeding fine?
Of course, the easiest way of avoiding points and a fine is to check your speed at all times and keep within the speed limit. But with so much street furniture and so many distractions bombarding the average motorist, it’s not too hard to get caught out by a change in speed limit.
If you want added security, then a speed camera locator is the best piece of kit to use. We tested a batch of speed camera locators in 2018, with products from Road Angel and Snooper performing well, while apps from TomTom and Sygic were also well received.
Speed camera detectors use GPS location technology to warn you of fixed camera locations. In addition, the best units also feature laser and radar detecting technology to warn you of mobile speed camera sites, as well as those fixed locations that aren’t logged on to the device’s database. The best speed camera locators can show you your speed, as well as calculating your average speed within a SPECS average speed camera location. By Graham Hill with a big thanks to Auto Express